Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Healthcare, Hospitals and Medicine
Artificial intelligence holds great promise to help medical and healthcare professionals gain key insights and improve health outcomes. However, AI adoption in healthcare has been sluggish.
Despite the slow uptake of AI in healthcare, 85 percent of healthcare executives have an AI strategy, and almost half of executives now use the technology.
There is a deep need in healthcare organizations for AI to address healthcare problems such as chronic illness, workforce shortages and hospital readmissions. These factors lead ai in healthcare professionals, healthcare organizations themselves, insurance companies and pharma and life sciences organizations to adopt AI.
AI plays a role in improving data flow, recognizing and processing both structured and unstructured data.
New efficiencies are speeding up data analysis. AI identifies patterns, generating insights that might elude discovery from a physician’s manual efforts.
Why Use AI In Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies revolutionize healthcare and quality patient care delivery.
Health organizations have amassed massive amounts of patient health data, including electronic health records, medical images and photographs, electronic health records, demographic health data, health records, claims data, health records, and clinical trial data.
AI technologies are perfectly adapted to analyzing this data and uncovering patterns and insights humans could not independently discover.
“Deep learning and traditional machine learning and from AI may assist the whole healthcare industry, healthcare organizations, healthcare payers themselves, medical professionals and healthcare organizations in making better financial and clinical choices and improve the quality of the experiences they give.
How AI Is Used In Healthcare
AI can analyze enormous volumes of healthcare data maintained by healthcare providers and organizations in the form of photographs, clinical data, research and clinical trials, and medical claims and can uncover patterns and insights that manual human skill sets cannot discern.
AI algorithms are “taught” to recognize and categorize data patterns, whereas NLP enables them to separate pertinent data patterns and relevant data together.
Data is analyzed and interpreted by deep and machine learning computers using deep and machine learning extended knowledge in DL.
According to a Frost & Sullivan report, artificial intelligence, or machine learning and deep, machine learning and other machine learning and deep learning, algorithms and cognitive computing systems in the healthcare industry will contribute $6.7 billion in market revenue this year, up from $811 million in 2015.
Natural Language Processing in Healthcare AI
Natural language processing (NLP) is an artificial intelligence technique that allows computers to comprehend and utilize human and natural language processing.
This type of technology has altered numerous industries, including healthcare. Natural language processing is utilized in various health and data science applications in healthcare, including enhancing patient care through improved diagnostic accuracy, optimizing clinical processes, and healthcare payers offering more personalized services.
For example, by extracting meaningful information from health data, natural language processing. It may be used in medical records to detect ailments effectively. It may also be used to find appropriate treatments and drugs for each patient and anticipate prospective health hazards based on historical health data. Furthermore, NLP provides powerful tools for clinicians to manage large amounts of complex patient data, normally taking much longer to do manually.
Top 10 Applications of AI in Healthcare
1. AI Assists In Medical Imaging Analysis
AI is employed as ai in healthcare, ai case triage tool and ai technology in precision medicine. It aids a physician in evaluating ai in healthcare because of photos and scans. This allows radiologists and cardiologists to mine imaging data and find crucial insights to prioritize critical patients, avoid potential mistakes in reading electronic health records (EHRs), and make more exact diagnoses.
A clinical investigation can generate massive volumes of data and photographs that must be verified. AI systems may quickly analyze these datasets and compare them to other research to uncover patterns and out-of-sight links. The procedure enables medical and imaging professionals and healthcare providers to track critical information immediately.
Patient Synopsis examines previous diagnostics and other medical imaging histories, imaging radiology images, procedures, test findings, medical history, and current allergies to provide radiologists and cardiologists with a summary focusing on the context of these pictures. The product may be incorporated into any medical unit system structure, accessible from any communication workstation or device on the network, and upgraded without interfering with the medical unit’s daily operations.
Detecting pertinent concerns and presenting them to radiologists in an easy-to-read summary format allows for creating more customized, focused, and accurate reports in the diagnostic decision-making process.
2. AI Reduces The Cost Of Drug Development
Supercomputers have been used to forecast which medications would and would not be beneficial for certain ailments based on databases of molecular structures.
AtomNet could predict the binding of tiny chemicals to proteins by analyzing indications from millions of experimental data and thousands of protein structures using convolutional neural networks, a technology similar to that used to construct artificial intelligence for self-driving automobiles and artificial intelligence.
Convolutional neural networks could select a safe and effective therapeutic candidate from the database examined, lowering the cost of creating pharmaceuticals.
During the West African Ebola virus epidemic in 2015, Atomwise collaborated with IBM and the University of Toronto to screen the top compounds capable of binding to a glycoprotein that blocked Ebola virus entry into cells in an in vivo (in an animal or plant’s living body) test.
The drug used was chosen from those examined because it functioned on other viruses using a similar mode of cell penetration. This AI analysis took less than a day, a procedure that would normally take months or years, allowing for the creation of an Ebola virus cure. Same happened in 2020 with the pandemic of COVID-19.
3. AI Analyses Unstructured Data
Clinicians frequently struggle to keep up with the newest medical developments while providing quality patient-centered care owing to massive volumes of health data and medical records.
EHRs and biological data compiled by medical units and medical experts may be promptly examined by ML technology to give medical professionals and physicians with clinical documentation timely, trustworthy replies for daily clinical practice, healthcare research, and medical diagnosis.
In many situations, patient health data and medical records are kept as sophisticated unstructured data, making them difficult to comprehend and access.
Instead of being buried under the weight of searching, identifying, collecting, and transcribing the solutions they need from piles of paper-formatted EHRs, AI can seek, collect, store, and standardize medical data regardless of format, assisting repetitive tasks and supporting clinicians with fast, more accurate diagnoses financial outcomes, and, tailored treatment plans and medicine for their patients.
4. AI Creates Complicated And Integrated Drug Discovery Systems
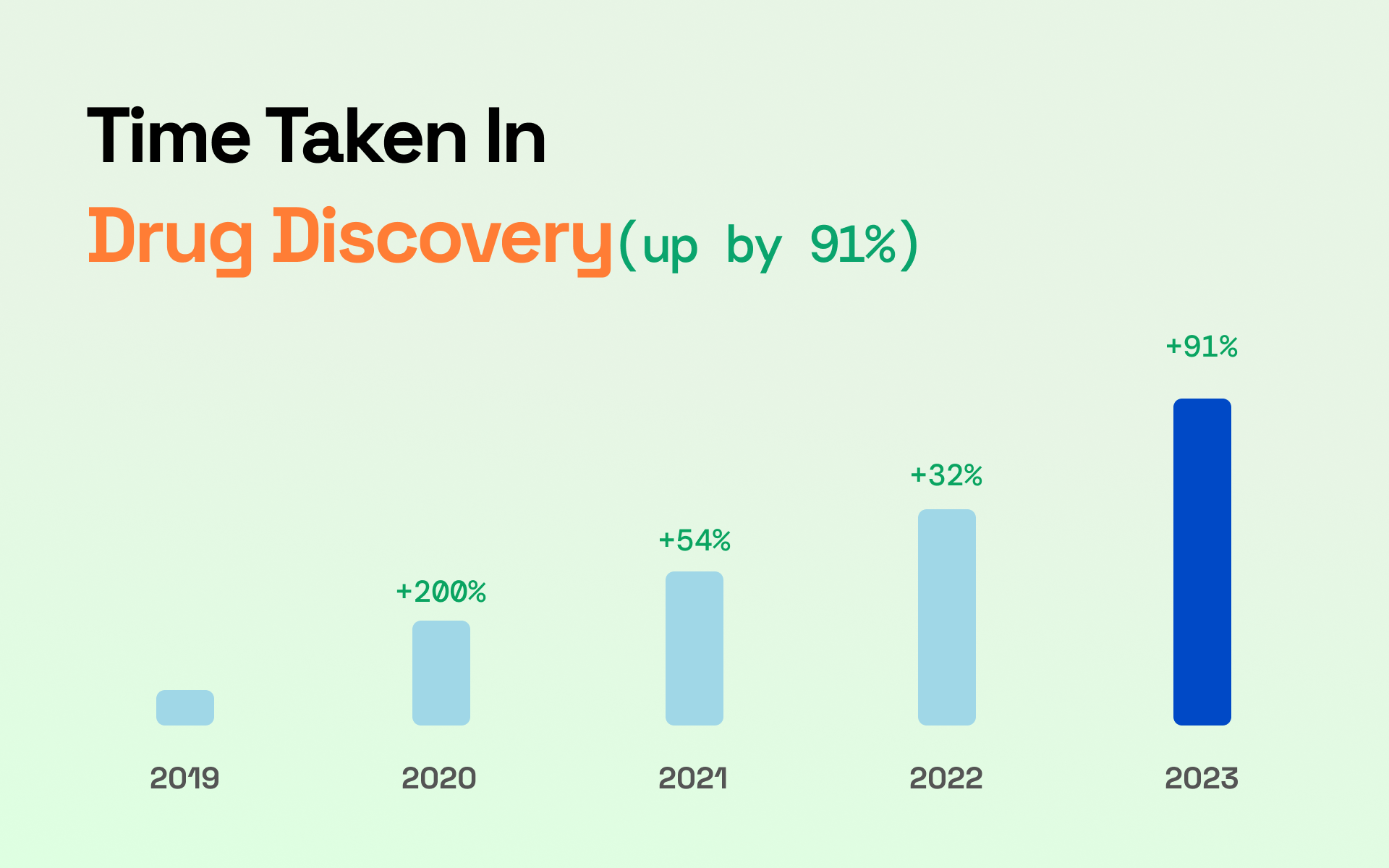
AI algorithms can find novel therapeutic applications, identifying their hazardous potential and action methods.
This technique created a drug discovery platform allowing the business to reuse pharmaceuticals and bioactive chemicals.
The original business of this platform can create roughly 80 terabytes of biological data analyzed by ai systems and AI tools across 1.5 million clinical trials, weekly by merging the greatest components of biology, data science, and chemistry with automation and the most recent AI developments.
The ML techniques are designed to extract insights from biological datasets that are too complicated for human interpretation, reducing the possibility of human bias.
Identifying new uses for current pharmaceuticals is an enticing approach for Big Pharma corporations since it is less expensive to repurpose and reposition existing treatments than to generate them from scratch.
5. AI Helps Diagnose and Manage Kidney Disease
Acute kidney damage (AKI) can be difficult for physicians to diagnose, but it can cause patients to worsen quickly and become life-threatening.
With an estimated 11% of hospital mortality caused by a failure to detect and treat patients, early prediction and treatment of these instances can significantly influence reducing life-long care and the expense of renal dialysis.
In 2019, the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and DeepMind Health developed a machine learning (ML) technology that can predict AKI up to 48 hours in advance. The AI algorithm identified more than 90% of acute AKI cases 48 hours sooner than standard treatment application diagnosis techniques.
The collaboration between VA and DeepMind Health continues. Its next goal is to figure out how to implement this ML tool in medical units.
A user-friendly interface is also being developed to assist physicians in making treatment decisions to enhance the quality of life for Veterans suffering from AKI.
6. AI Helps Emergency Medical Personnel
The time between the 911 call and the ambulance’s arrival is critical for recovery from a sudden heart attack.
To take the necessary steps, emergency dispatchers and medical professionals must be able to recognize the symptoms of cardiac arrest. AI can analyze verbal and nonverbal cues to diagnose from afar.
Corti is an AI tool that supports emergency medical personnel. Corti identifies a heart attack by analyzing the caller’s speech, background noise, and pertinent patient medical history data.
Like other ML systems, Corti does not look for specific signals but trains itself by listening to many conversations to find important elements.
Corti continuously updates its model based on this knowledge. Corti’s system can distinguish between background noise, like sirens, and caller or patient noises in the background.
In Copenhagen, emergency dispatchers can detect a cardiac arrest 73% of the time based on the description supplied by the caller.
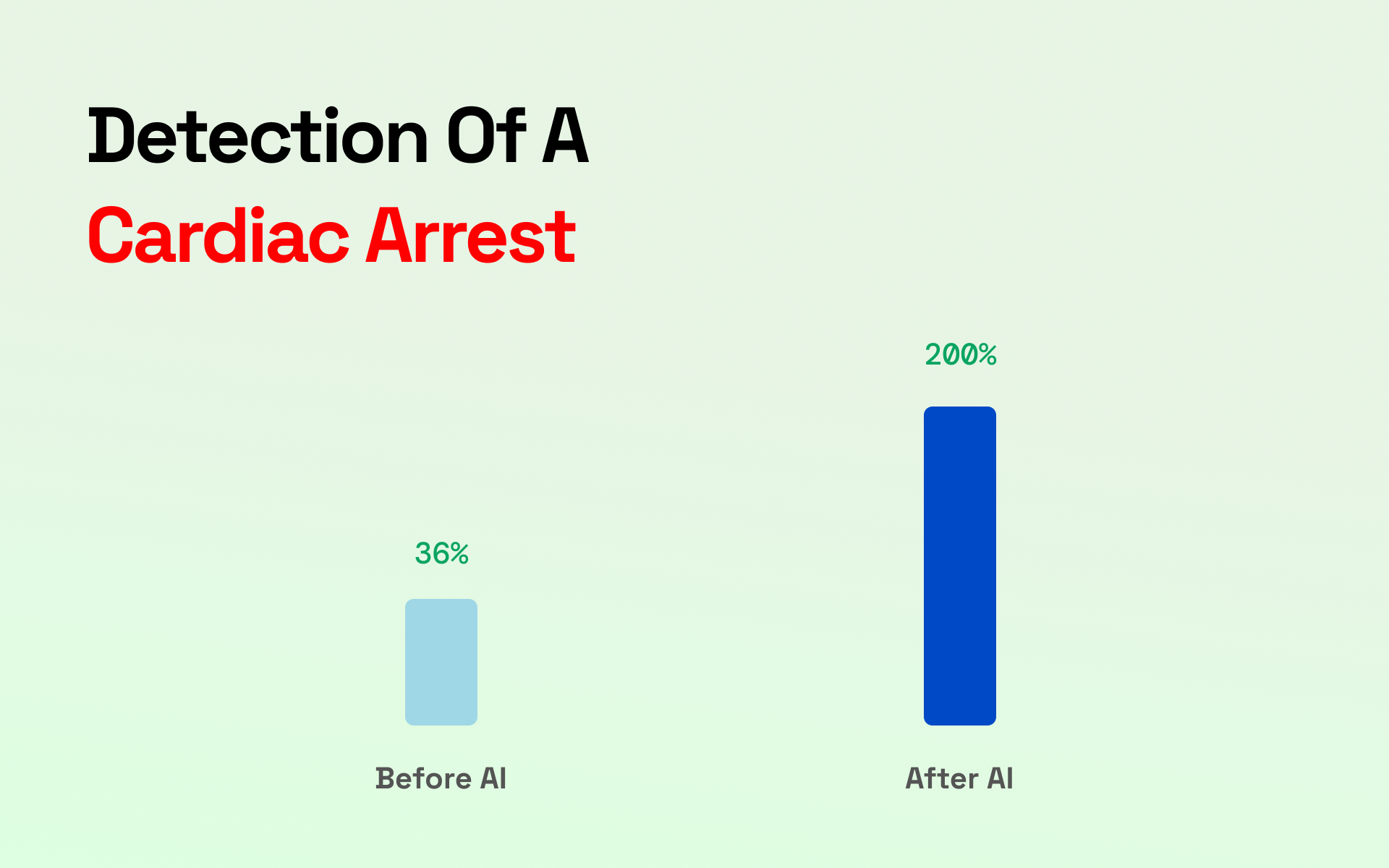
But AI can do better. A small-scale study done in 2019 discovered that ML models could recognize cardiac arrest calls better than human dispatchers utilizing voice recognition software, ML, and other background information.
ML can be quite useful for both medical professionals and assisting emergency medical personnel. In the future, medical units might employ the technology to react to emergency calls using defibrillator-equipped drones, medical professionals or CPR-trained volunteers, increasing the odds of survival in cardiac arrest situations in the community.
7. AI Assists Cancer Research and Treatment
In certain circumstances, radiation therapy may lack a digital database to gather and organize EHRs, making cancer research and treatment problematic.
Oncora Medical provides healthcare professionals with a platform that collects relevant medical data from patients, evaluates the quality of care, optimizes treatments, and provides comprehensive oncology outcomes, data, and imaging to help clinicians make informed decisions about radiation therapy for cancer patients.
The automatic creation of clinical notes and EHRs reduced doctors’ time managing medical records, monitoring patient health, patient and medical records management, and paperwork, and improving medical operations and other healthcare outcomes.
8. AI Uses Obtained Data For Predictive Analyses
By transforming EHRs into an AI-driven prediction tool, physicians may be more efficient in their workflows, medical choices, and treatment plans.
NLP and ML may read a patient’s entire medical history in real-time and associate it with symptoms, chronic affection, or sickness that affects other family members.
They can use the data to make medical devices and create a predictive analytics tool to detect and cure diseases before they become life-threatening.
In essence, chronic illnesses may be predicted and their development rates tracked. CloudMedX is a startup specializing in decoding unstructured healthcare data and data stored therein, such as notes (clinician notes, discharge summaries, diagnostic and hospitalization notes, and so on).
These notes are used with EHRs to produce clinical insights for medical practitioners, enabling data-driven decisions to enhance patient outcomes.
CloudMedX solutions have already been used in several high-risk diseases, including renal failure, pneumonia, congestive heart failure, hypertension, liver cancer, diabetes, orthopedic surgery, and stroke, to improve health outcomes and lower costs for patients, medical providers and clinicians by assisting in early and accurate diagnosis of patients.
9. AI Accelerates The Discovery And Development Of Genetic Medicine
AI is also used to swiftly identify and produce drugs, with a high success rate. Alterations in molecular phenotypes, such as protein binding, favor genetic disorders.
Anticipating these changes entails anticipating the emergence of genetic illnesses. This is feasible by gathering data on all identified chemicals, clinical processes, and biomarkers relevant to specific clinical studies.
Deep Genomics’ AI system, for example, processes this data.
The business develops proprietary AI and utilizes it to mine patient data in managers to uncover novel approaches to repair the effects of genetic mutations and produce customized medicines for those suffering from uncommon Mendelian and complicated illnesses.
The business is testing discovered chemicals to produce speedier genetic therapy for illnesses with high unmet needs.
The company’s experts are working on “Project Saturn,” a drug system based on AI molecular biology that evaluates more than 69 billion oligonucleotide molecules in silico (conducted or produced using computer modeling or computer simulation) against 1 million target sites to monitor cell biology and unlock more potential treatments and therapies.
The discovery and development of genetic medicine benefit patients and physicians by lowering the expenses involved in treating uncommon illnesses.
10. AI Promotes Health Equity
The AI and ML sector is responsible for designing healthcare systems and technologies that guarantee justice.
Equality is addressed in the healthcare industry and benefits from substantial integration projects, ai technologies, data science and clinical trials to give the best possible health results. The increased usage of ML algorithms in healthcare industry benefits numerous fields, only healthcare providers and ai technologies, and the adoption of precision medicine raises the possibility of better health outcomes and disparities.
Those in charge of deploying AI in the healthcare research industry must guarantee that AI algorithms are accurate, impartial, and fair. Because many clinical trial guidelines and diagnostic tests take data managers a patient’s race and ethnicity into account, a debate has erupted:
Is the selection of these elements evidence-based? Is data on race and ethnicity more likely to alleviate or exacerbate universal health care disparities? It has been demonstrated that ML is a collection of strategies that allows computers to learn from the data they analyze.
In theory, ML may produce unbiased forecasts based only on an impartial study of the underlying facts.
By fostering data transparency and diversity, AI and ML systems may be trained to reduce or eliminate prejudice, lowering mental health and inequalities.
AI and other machine learning algorithms and deep learning models in healthcare can eradicate health-outcome disparities based on race, ethnicity, or gender.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
As the capabilities of artificial intelligence in healthcare have expanded, utilizing it to improve medical practices has become more feasible.
The potential for applying AI in healthcare is infinite, thanks to the development of AI-powered medical equipment and clever algorithms capable of interpreting massive medical data sets.
Deep learning AI may be used to diagnose diseases more quickly, give personalized treatment plans, and even automate procedures like drug research and testing. It also has the potential to improve patient outcomes, increase safety, and lower healthcare delivery costs.
The future of artificial intelligence in healthcare is unquestionably bright and full of opportunities for further innovation.
As we go towards a more connected digital world, integrating AI into the healthcare business will become a significant tool that has the potential to transform how doctors treat patients and provide care.
With such enormous potential, it is evident that implementing artificial intelligence in healthcare promises a future filled with innovations, improved health outcomes, and ai in health and enhanced patient experiences.
The most difficult hurdle for AI in healthcare is assuring its acceptance in daily clinical practice, not whether the technologies will be capable enough to be useful.
Medical practitioners may eventually gravitate towards duties that need unique human talents, such as the greatest degree of cognitive function.
The only other healthcare organizations and providers who will miss out on AI’s full potential in healthcare are those who refuse to collaborate with it.